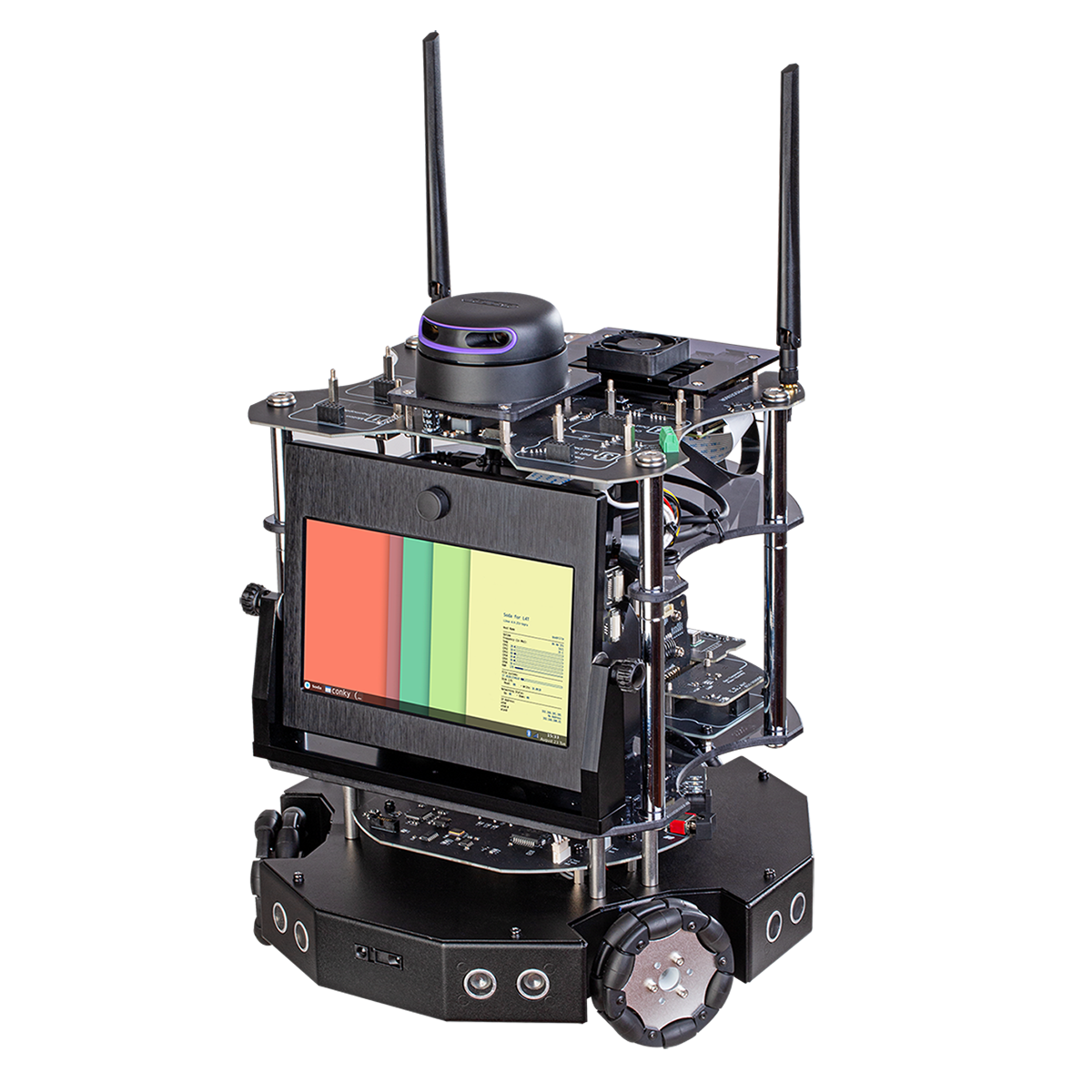
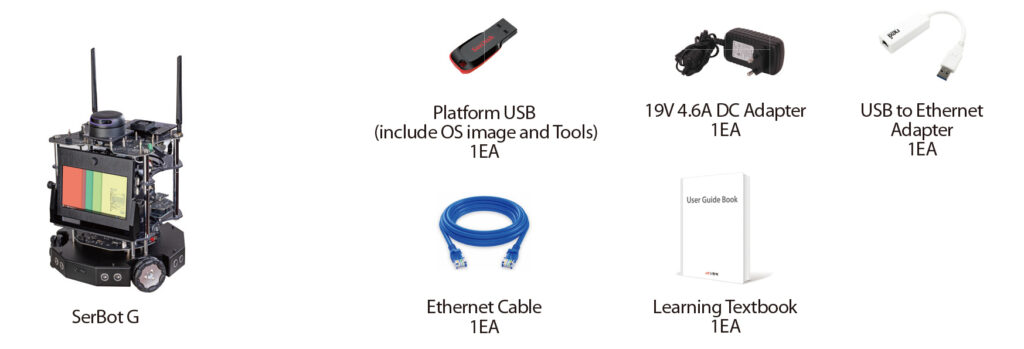
Product Features
- AI application practice equipment based on indoor service robot platform
- Main processor is GPU supercomputer platform for edge device
- 7-inch touch display with 1024×600 resolution and 8M pixel 160° wide-angle camera
- Gigabit Ethernet, dual-band Wi-Fi (2.4GHz, 5GHz), and Bluetooth 4.2
- Voice recognition and audio play through digital microphone and speaker
- Supports various IoT sensor modules through four exclusive expansion interfaces
- 3-axis omni wheel to maximize the movement efficiency and minimize the turning radius
- Multiple PowerPath blocks allowing to practice even while the battery is charging
- Robot standard middleware ROS2 and Pop library are provided
- Supports CUDA-based PyTorch and Tensorflow artificial intelligence framework
- Supports web browser-based Google block coding platform (Blockly)
- Supports a public integrated development environment based on Visual Studio Code for professional application development
- Service robot learning content based on artificial intelligence and deep learning is provided
Software Specifications
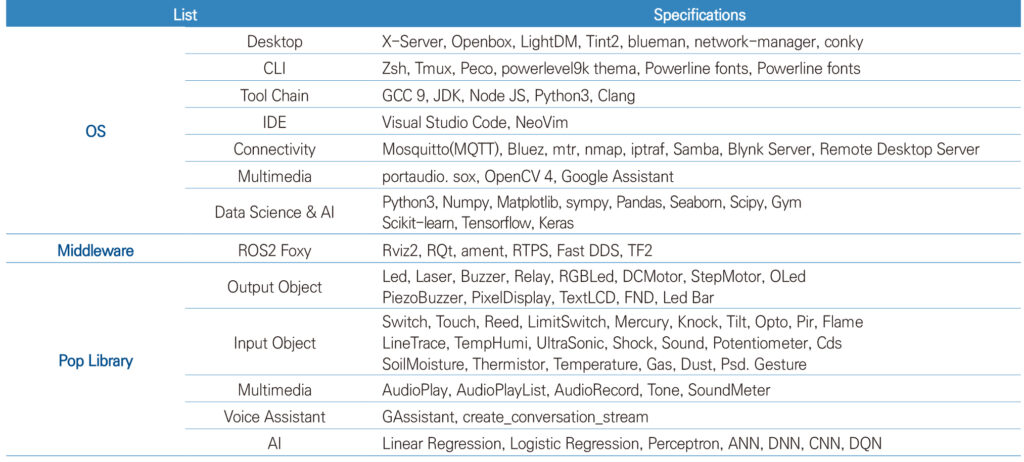
Training Contents
- Artificial Intelligence and Autonomous Driving
- 1.1. Components of Autonomous Driving
- 1.2. Autonomous Driving Overview
- Environment for Experiment
- 2.1. AIoT SerBot-G
- 2.2. Communication between PC and AIoT SerBot-G
- 2.3. Development Environment
- Control AIoT SerBot-G
- 3.1. 3WD Omni Wheel Moving Device
- 3.2. 9DOF IMU Sensor
- 3.3. Ultrasonic Sensor
- 3.4. Psd Sensor
- CAN Protocol
- 4.1. CAN Network
- 4.2. CAN Communication
- 4.3. CAN Communication in Linux
- 4.4. Example of CAN Protocol Application
- Moving Device Library based on CAN Communication
- 5.1. Start Library
- 5.2. Moving Device Control Library based on CAN Communication
- 5.3. Implement Sensor Action and Broadcast Reception
- MQTT
- 6.1. MQTT Standard
- 6.2. MQTT Broker and Client
- 6.3. Topic
- 6.4. Session
- 6.5. MQTT Development Environment
- 6.6. Remote Control of MQTT Moving Device
- LiDAR
- 7.1. LiDAR Sensor
- 7.2. LiDAR Control
- 7.3. Avoidance Driving using LiDAR
- Artificial Intelligence
- 8.1. Machine Learning and Perceptron
- 8.2. Neural Network and Learning
- 8.3. Machine Learning Framework
- Autonomous Driving
- 9.1. Vision Processing
- 9.2. Deep Learning and Convolutional Neural Network
- 9.3. Lane Recognition based on Deep Learning
- 9.4. Object Detection and Moving Object Control
Appendix
- A. Flame Sensor
- B. PIR Sensor
- C. ECO Sensor
- D. CO2
- E. Dust Sensor
- F. Thermopile Sensor
- G. Micro Wave Sensor
- H. Peripheral
- I. Pixel Display
Layout
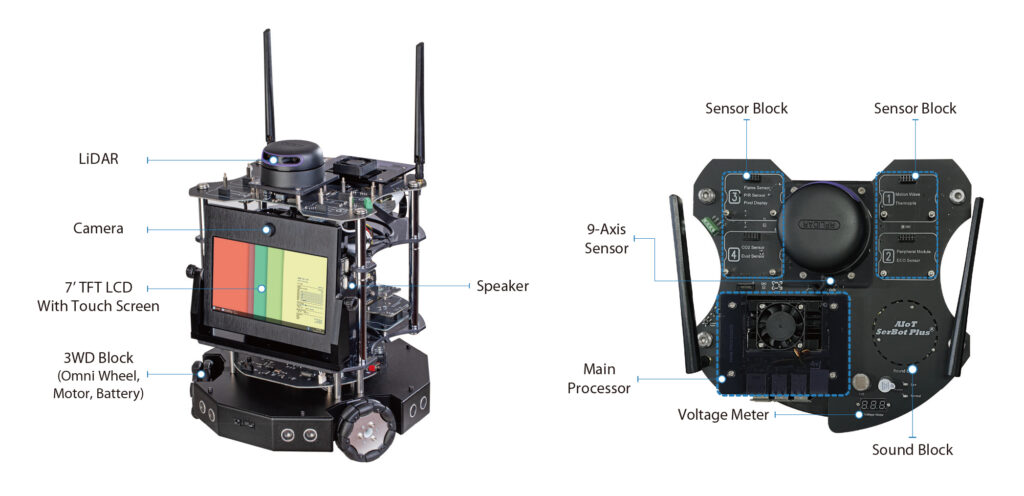
Components